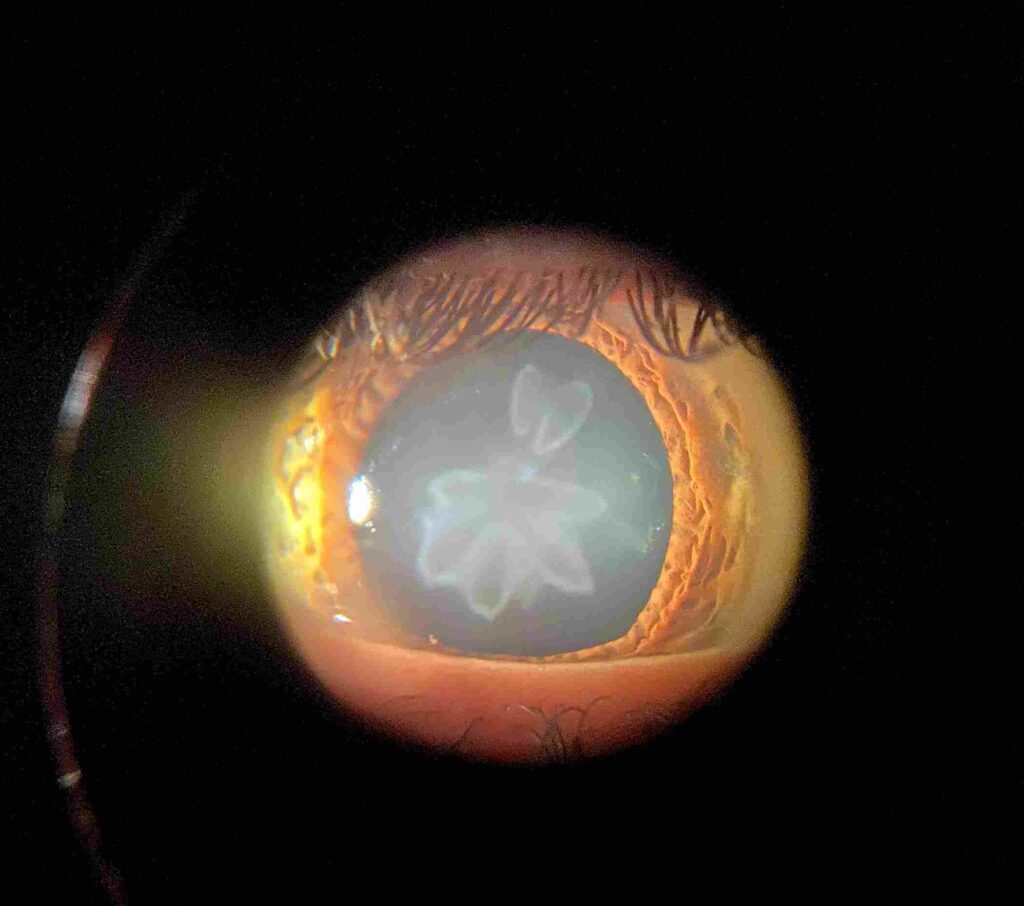
A rosette cataract is a type of cataract that appears as a circular or radial spoke-like lesion on the posterior capsule. It is often associated with an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) and can lead to vision loss if left untreated. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes and symptoms of rosette cataracts, as well as how they can be managed.
What Is A Rosette Cataract?
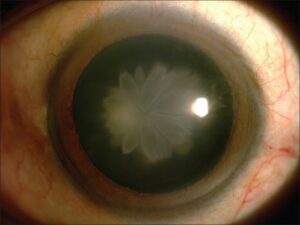 A rosette cataract is a type of congenital cataract that is characterized by a radial array of opacities surrounding the pupil. Rosette cataracts are usually found in infants and young children. In simple words, this type of cataract is described as a “flower petal” shaped opacity on the child’s eye.
A rosette cataract is a type of congenital cataract that is characterized by a radial array of opacities surrounding the pupil. Rosette cataracts are usually found in infants and young children. In simple words, this type of cataract is described as a “flower petal” shaped opacity on the child’s eye.
It is also believed that rosette cataracts are caused by a genetic mutation. However, the exact gene responsible for this condition has not been identified yet. Some reports suggest that rosette cataracts may be associated with other eye abnormalities such as microphthalmia, coloboma, and/or nystagmus.
Studies have also found that rosette cataracts are more common in certain ethnic groups such as Asians and Native Americans. However, it is not clear why this is the case. Moreover, it is important to note that rosette cataracts can occur in any race.
Therefore, you should take your child to the doctor if you notice any changes in their vision. If left untreated, rosette cataracts can cause serious vision problems such as amblyopia (lazy eye) and strabismus (crossed eyes). So, do not hesitate to get your child’s eyes checked by a doctor if you think they may have this condition.
Are There Any Types Of Rosette Cataracts?
Probably yes, there are a few types of rosette cataracts. These are congenital, developmental, and acquired. Let’s understand each one of them in detail.
Congenital rosette cataracts are those that are present at birth. They can be hereditary or non-hereditary. Hereditary rosette cataracts are usually passed down from parents to children. Non-hereditary congenital rosette cataracts can be caused by infections, trauma, or certain medications during pregnancy.
Developmental rosette cataracts occur later in life and are usually the result of an injury to the eye. It is also possible for them to be caused by certain diseases or conditions, such as diabetes.
Acquired rosette cataracts are those that develop over time. They are most often seen in older adults and can be the result of years of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, smoking, or other environmental factors. These can be caused by diseases, aging, or exposure to toxins or radiation.
So it is important to understand each type in order to manage the condition better. You will be able to find more information on the internet or from your doctor.
Symptoms To Identify Rosette Cataract
Identifying symptoms is the first step in managing rosette cataracts. The most common symptom is vision impairment, which can manifest as blurriness, double vision, or light sensitivity. Other symptoms include:
- seeing floaters or halos around objects
- changes in the appearance of colors
- difficulty with night vision
- sudden onset of symptoms
- frequent changes in the prescription of eyeglasses
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see an eye doctor right away. They will be able to diagnose rosette cataracts and develop a treatment plan. Moreover, it is important to manage the condition because it can progress and lead to more serious symptoms, such as blindness.
There is no cure for rosette cataracts, but there are treatments that can help improve vision. With the help of a professional, you can develop a plan that is right for you.
Causes And Risk Factors
 It is important to know the causes and risk factors of rosette cataracts to properly manage the condition.
It is important to know the causes and risk factors of rosette cataracts to properly manage the condition.
Rosette cataract is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for connexin 50 (CX50), a protein that is essential for the proper development and function of the eye lens. The CX50 gene is located on chromosome 13. The mutation that causes a rosette cataract is usually passed down from a parent to a child. However, in some cases, the mutation can occur spontaneously.
People with certain medical conditions are at increased risk of developing rosette cataracts. These conditions include:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Galactosemia
- Lowe syndrome
- Nance-Horan syndrome
- Stickler syndrome
Along with these, there are also some risk factors that can increase the chances of developing rosette cataracts. These include:
- force trauma to the head
- trauma to the eyeball
- hemorrhage or eye bleeding
- exposure to radiation
If you have any of these risk factors, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of rosette cataracts so that you can seek treatment as soon as possible.
How Does It Impact Everyday Life?
When someone has a rosette cataract it can have a big impact on their everyday life. Some of the negative consequences that rosette cataracts might have include:
- Sufferers might have difficulty with their vision, which can make it hard to do things like reading or driving.
- The condition can also cause headaches and dizziness.
- In some cases, people with rosette cataracts might even experience nausea.
If left untreated, rosette cataracts can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Glaucoma: This is a condition in which the pressure inside the eye becomes too high. This can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss.
- Corneal ulcers: These are sores on the surface of the eye. They can be painful and may lead to vision loss.
- Retinal detachment: This is when the retina, which is the layer of tissue at the back of the eye, pulls away from its normal position. This can cause vision loss or even blindness.
As you can see, a rosette cataract can have a serious impact on a person’s quality of life. If you or someone you know has this condition, it is important to get treatment as soon as possible. Moreover, it is also important to try and manage the condition with lifestyle changes and by following the advice of your doctor.
As this condition can have such a big impact on someone’s life, it is important to be as proactive as possible in managing it. With the right help, you will be able to manage the condition and live a normal, healthy life.
How Rosette Cataract Is Treated?
 The treatment options for rosette cataracts are limited. Here are some methods that have been used to manage this condition:
The treatment options for rosette cataracts are limited. Here are some methods that have been used to manage this condition:
- Corticosteroids can be used to reduce inflammation and help shrink the size of the cataract. This can improve vision but will not get rid of the cataract completely. Because it is a temporary measure, it may need to be repeated several times.
- Cataract surgery is the only way to remove the cloudy lens and improve vision. This can be done with a traditional approach or with a laser. Also, it is important to note that not all people with rosette cataracts will need surgery. But it is something to consider if your vision is significantly affected.
There are standard surgery types like extracapsular extraction (ECCE) and phacoemulsification that can be used to remove cataracts. But there are also newer, less invasive methods being developed, such as laser-assisted surgery.
In some cases, a contact lens or glasses may be all that is needed to improve vision. This is because the cloudiness of the lens is not always in the center, which is where it would cause the most problems with vision.
If you have rosette cataracts, talk to your doctor about the best treatment options for you. There is no one-size-fits-all approach, so it is important to find what works best for you.
Tips To Prevent Rosette Cataract
There are certain things you can do to help prevent rosette cataracts:
- Wear sunglasses when outdoors to protect your eyes from the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays.
- Eat a healthy diet that includes foods rich in antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E.
- Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your risk of developing cataracts.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise helps to improve circulation and overall health, which can help reduce your risk of developing cataracts.
- Regular checkups. It is important to have regular eye exams so that your doctor can check for any changes in your vision or the health of your eyes.
So these are some of the prevention tips for rosette cataracts. Following these tips may help you to keep this disease at bay. However, if you already have cataracts, surgery is the only way to remove them. Cataract surgery is a very common and safe procedure that can help improve your vision. If you think you might have cataracts, make an appointment with your eye doctor to have them checked out.
Conclusion
Conclusively, a rosette cataract is defined as a form of a cataract where the lens appears to have a series of radial spoke-like opacities. They are generally asymptomatic and do not require treatment. However, in some cases, they can cause decreased vision. But, you should not worry if you or your loved one has been diagnosed with a rosette cataract.
In most cases, they are harmless and will not cause any vision problems. But, if you are experiencing symptoms, be sure to contact your eye care professional right away. With proper management and treatment, you can protect your vision and live a healthy life. You can also contact EyeMantra for more information and resources.
At EyeMantra we have a team of experienced eye surgeons, who will be happy to answer your questions on cataract surgery, cataract surgery cost, and cataract lens cost for different cataract surgery types- Phacoemulsification, MICS & Femto Laser Cataract. Call us at +91-9711116605 or email at [email protected] for inquiries.